A story that Greeks are all too familiar with, Alexander the Great solidified his place in the history books at this time in 334 BC, when he crossed the Hellespont and began his historic campaign in the East.
While it is unknown of the exact date, it is recorded that he began his campaign in the middle of Spring, with April 1 signifying the beginning of the second month of Spring in Greece.
Brief Background
The earliest known account of Alexander’s life is by the Greek historian Diodorus, but we also have histories written by other historians, regarded as the Alexander historians. They interpreted written accounts from shortly after Alexander’s death, penned by those who fought alongside Alexander on his campaigns.
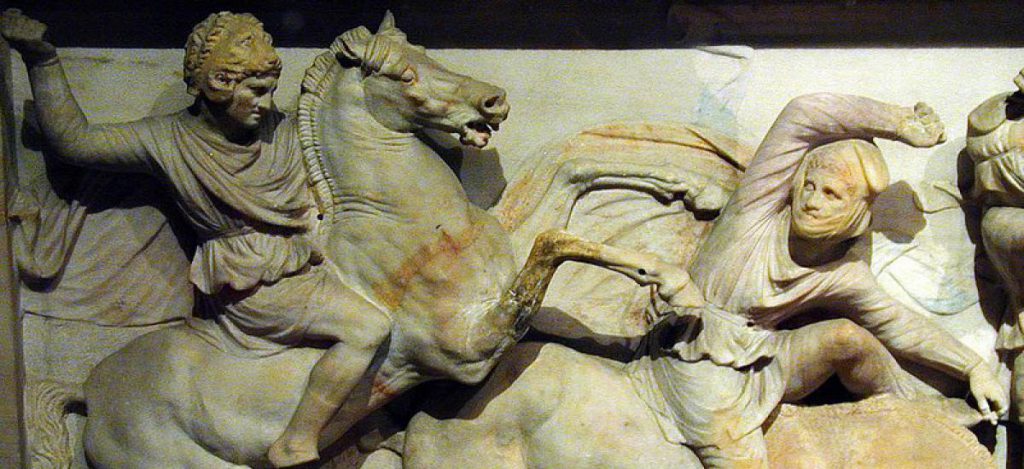

Alexander was born in Pella, the capital of the Kingdom of Macedon. He was the son of the king of Macedon, Philip II, and his fourth wife, Olympias. Philip II of Macedon – who reigned from 359 to 336 BCE – was an accomplished king and military commander in his own right. Inheriting a weak, underdeveloped society, he moulded Macedon into a military nation that subjugated most of Greece.
In 336 BCE, after King Philip II of Macedon was killed, Alexander was quickly crowned as the king. After subduing any serious threats to his rule, and with the Greek city-states now firmly under Macedonian rule following Charonea, Alexander embarked on the great campaign his father had been planning: the conquest of the mighty Persian Empire.
The Campaign Begins
Alexander the Great took over the already existing invasion project of Philip II, who had sent Parmenion, with Amyntas, Andromenes and Attalus, and an army of 10,000 men into Anatolia two years prior. Alexander’s army crossed the Hellespont in 334 BC with approximately 48,100 soldiers, 6,100 cavalry and a fleet of 120 ships with crews numbering 38,000. The men were drawn from Macedon and various Greek city-states, mercenaries, and feudally raised soldiers from Thrace, Paionia, and Illyria.
Crossing the Hellespont, Alexander the Great showed his intent to conquer the entirety of the Persian Empire. The commander threw a spear into Asian soil, saying he accepted Asia as a gift from the gods. At this point, a war was declared with the lands of the East.

His initial victory against Persian forces at the Battle of the Granicus, was the first of many, as Alexander accepted the surrender of the Persian provincial capital. He then proceeded along the Ionian coast, granting autonomy and democracy to the cities.
Alexander was a unique king, unlike any before seen in Europe. As he expanded beyond Persia into Asia Minor, Syria, Egypt, Mesopotamia, and Bactria, he did not drastically challenge existing administrative systems. Rather, he adapted them for his own purposes and used the cities as defensive garrisons administrative headquarters.
Unlike any previous conquerer, Alexander was not interested in imposing his own ideas of truth, religion, or behaviour upon newly ruled territories. As long as citizens of these nations kept supply lines open to feed his troops, he encouraged the trade and spread of different cultures.
Despite this, Alexander spread the value of Greek culture which was impressed upon him by his tutor, the Greek philosopher Aristotle (384-322 BCE). As Alexander campaigned, he spread Greek thought and culture in his wake, thus creating the “Hellenistic World”.
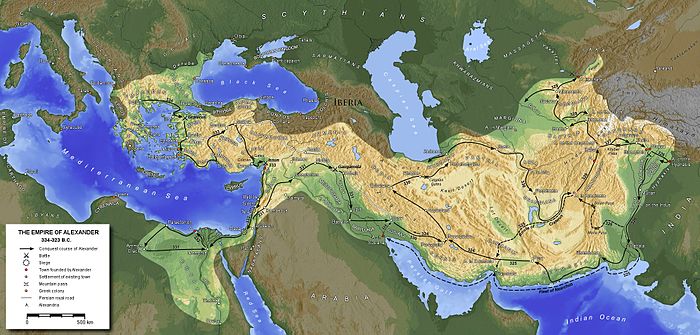
To create this dream, Alexander was not shy of violence and victory through ruthless measures. With Alexander’s campaign through the East lasting for over 10 years, it is expected that him and his army killed at least 150,000 soldiers, many of them Persian.
Alexander the Great’s conquest sadly did not end on his own terms, rather from the mutiny of his own troops. The Greek commander turned his attention towards India in 327 BCE, yet his exhausted troops refused to go farther. The troops remained in the conquered regions of Persia and Asia Minor.
Legacy And Memory
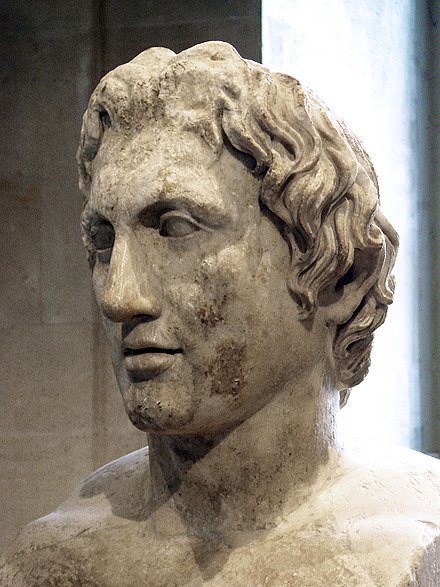

Mystery still surrounds Alexander the Great’s death to this day. Many historians assume that the Greek leader died of disease, yet the real cause is truly unkown. Alexander the Great died in June 323 B.C. at age 32 with no successor to his throne line.
Many conquered lands retained the Greek influence Alexander introduced, and several cities he founded remain important cultural centers even today. The period of history from his death to 31 B.C., when his empire folded, would come to be known as the Hellenistic period, from “Hellazein,” which means, “to speak Greek or identify with the Greeks.”
Alexander the Great is revered as one of the most influential leaders the ancient world ever produced, and an icon for every Greek citizen.
Sourced by:
- Alexander the Great. Ancient History Encyclopedia.
- Alexander the Great. Livius.org.
- Alexander the Great of Macedon Biography. Historyofmacedonia.org.
- Alexander the Great. History.com

