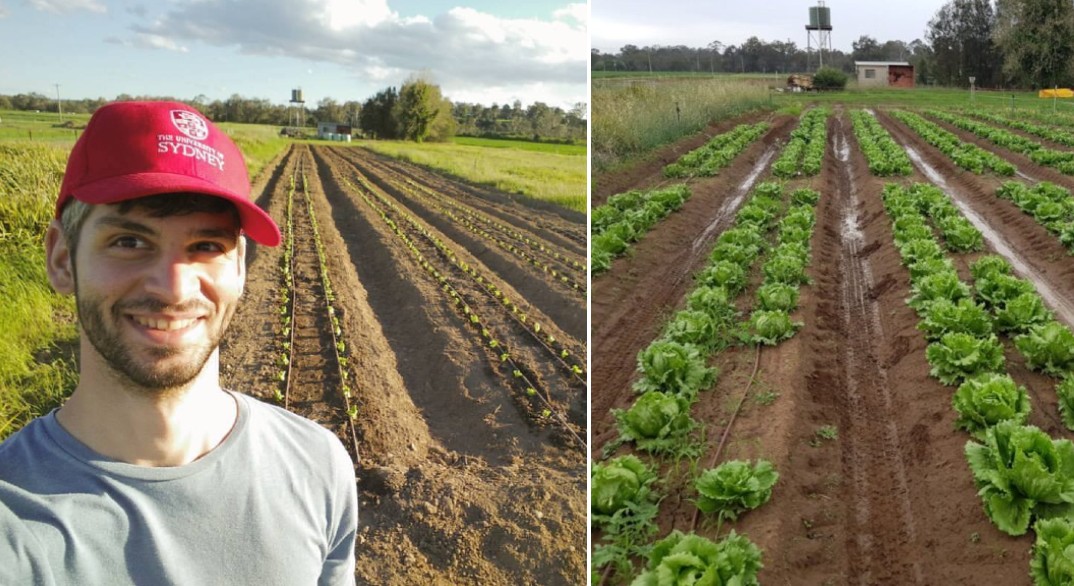
Robotics expert Steven Potiris recently completed his PhD thesis, exploring ways to improve the efficiency of crop mapping on a national scale.
Crop mapping can allow national and multinational agricultural agencies, insurance agencies, and regional agricultural boards to prepare an inventory of what was grown in certain areas and when. Providing phenotype data for breeding research, the system must be able to detect and segment each plant from its background.
“They breed two crops together in the hopes of making some kind of genetic gains, for example making them more resistant to drought or making them produce larger plants faster,” Steven said.
“But the problem is that when you breed plants, one single plant can have a lot of variations. And so you don’t typically want to just breed two plants and go ‘let’s see if this works’.”
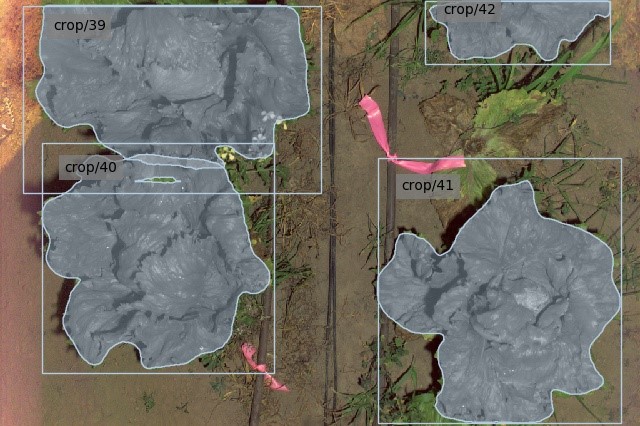
An example of a result of the developed instance segmentation model, which allows the accurate association of phenotypic traits to each individual plant.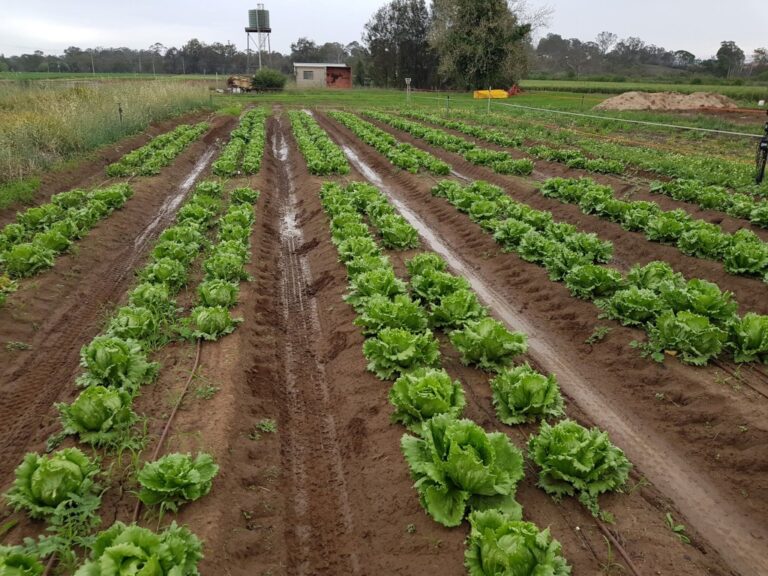 
Rows of iceberg lettuce grown in both crop- and weed- overlap conditions, which presents significant challenges to segment plants individually.
Steven says that these tests need to be conducted on a large scale, due to the amount of variability that can occur. Currently, tests such as these are conducted in indoor research farms and research facilities.
“It’s not very cost effective. You typically are always operating at a loss in that way,” Steven said.
“There are multiple reasons for that, and sone of them is that it’s actually very hard to measure the crops.”
Explained in his thesis, Steven has designed an unmanned ground vehicle to produce some of these measurements, attributing phenotype measurements from an RGB camera to individual plants.
“By doing that, you can increase your sample size to thousands, hundreds of thousands and still be in a commercial environment where that crop is also saleable.”
Various inputs (water, herbicides and nitrogen) were applied in an experiment to create a diverse dataset among cos and iceberg lettuce, broccoli and cauliflower crops. The labelled datasets are used to train both implicit and explicit instance segmentation models, and the results are compared against crop-crop and crop-weed overlap factors.

According to the Australian Government Health Department, there are currently three genetically modified (GM) crops that are grown in Australia: cotton, canola and safflower. All GM crops grown in Australia (commercial and experimental) is approved by the Regulator only if a scientific assessment shows that they are safe for people and the environment.
According to Steven, the university didn’t give permission for any of the 2000 crops planted to be eaten or taken home, in accordance with current crop development laws.
Steven’s thesis paves the way for the use of unmanned vehicles to be a vital asset in the production of crops on a large, national scale.
“Many people don’t actually know how prolific in everyday life crop breeding is,” Steven said.
“I would say definitely there’s a large proportion of of crops which have been successfully bred using older methods, and basically the benefit of my work is that it can be applied to an outdoor setting in which it is commercially viable to do these experiments.
“You get the benefits of planting commercially and running your experiments at the same time… and with very little manual effort.”
